Investing in a new CNC machine is an exciting time for any manufacturing business. However, getting started with production can be overwhelming without the right tools and accessories. Whether you're new to the world of CNC machining or a seasoned pro, having the right equipment is essential to ensure the quality and efficiency of your work.
In this guide, we'll take a closer look at the necessary tooling, vices, and accessories you'll need to kick start production on your new CNC machine. From basic cutting tools to more specialized equipment, we've got you covered. So, let's dive in and explore the world of CNC machining and the tools you need to succeed.
Essential Tooling for a New CNC Machine: Get Your Workshop Ready
1. General Purpose Tooling
General purpose tooling is an essential part of starting production on a new CNC machine. These tools include end mills, cutters, inserts, drills, taps, and more. End mills are used to cut materials such as metal, plastic, and wood. They come in various sizes and shapes, such as ball end, square end, and corner radius. Cutters, on the other hand, are used to cut materials into specific shapes and sizes. They include face mills, slot drills, and more.
Inserts are another type of basic tooling that are used to perform various operations such as turning, milling, drilling, and threading. They are typically made of carbide or other hard materials and are designed to be easily replaceable. Drills are used to create holes in materials and come in different sizes and types such as twist drills, center drills, and spot drills.
Taps are used to create internal threads in materials such as metal and plastic. They are available in various sizes and types such as hand taps, machine taps, and spiral point taps. Other types of basic tooling that may be necessary for a new CNC machine include reamers, countersinks, and broaches.
When selecting basic tooling for a new CNC machine, it is important to consider factors such as material type, cutting speed, and depth of cut. The right tooling can improve production efficiency and reduce the likelihood of tool wear and breakage. Proper maintenance and storage of these tools can also extend their lifespan and improve their performance.

2. Special Purpose Tooling
In addition to basic tooling, special purpose tooling is also an important consideration for starting production on a new CNC machine. Advanced tooling includes tools such as boring bars, thread mills, and other specialized cutting tools.
Boring bars are used to create internal holes or enlarge existing ones. They are typically used to create holes with tight tolerances or unusual shapes. Thread mills are used to create threads in materials such as metal, plastic, and wood. They are available in various sizes and types, such as single-point thread mills and multi-tooth thread mills.
Other types of advanced tooling that may be necessary for a new CNC machine include special reamers, form tools, and grooving tools. These tools are designed to perform specialized tasks such as creating chamfers, grooves, or complex shapes.
When selecting advanced tooling for a new CNC machine, it is important to consider the material type and the specific cutting operations that will be performed. Advanced tooling may require specialized programming or setup procedures, so it is important to have knowledgeable personnel on hand to ensure proper use.
Proper maintenance and storage of advanced tooling is also important to ensure their longevity and performance. Regular inspection and calibration can help to identify wear or damage and prevent tool breakage or other problems during use.
3. Work Holding
Work holding is a critical aspect of CNC machining, as it directly impacts the accuracy and precision of the finished parts. The right work holding tools and techniques can ensure that parts are held securely in place and that machining operations are performed with precision.
One essential tool for work holding is the vice. Vices are used to hold parts securely in place on the machine table during machining operations. They come in various sizes and types, such as machine vices, drill press vices, and quick release vices. Fixtures are another type of work holding tool that are used to hold parts in place during machining. They may be customized to fit specific part geometries and can hold multiple parts simultaneously.
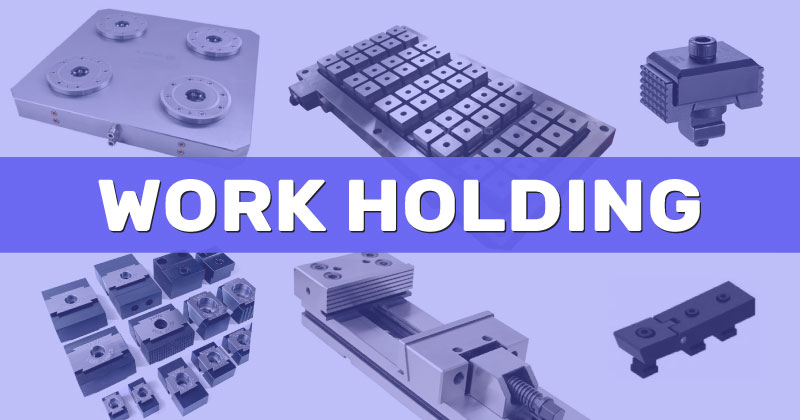
Zero points are a type of work holding system that use a base plate and a series of clamping elements to quickly and accurately locate and hold parts in place. They are often used in high-volume production settings and can reduce setup times and increase productivity.
Clamps are another essential work holding tool that are used to hold parts in place during machining operations. They come in various sizes and types, such as T-slot clamps, step clamps, and strap clamps. Parallel and angle plates are also commonly used work holding tools, as they provide a precise and stable reference surface for holding parts.
When selecting work holding tools for a CNC machine, it is important to consider factors such as part size and geometry, cutting forces, and machine table size and capacity. The right work holding tools can improve part accuracy and reduce the likelihood of part movement or vibration during machining operations.
In addition to selecting the right work holding tools, it is important to use proper techniques and procedures for work holding. This includes proper clamping force, surface preparation, and alignment. Regular inspection and maintenance of work holding tools can also help to ensure their longevity and performance.
4. Essential Measuring Equipment
Measuring equipment enables machinists to ensure that parts are produced with precision and accuracy. There are a variety of measuring tools and instruments that can be used on a CNC machine, including vernier calipers, micrometers, thread gauges, bore gauges, dial gauges, surface plates, and height gauges.
Vernier calipers are a type of measuring tool used to measure length, width, and thickness of parts. They consist of two arms that slide along a calibrated scale and can measure to within 0.1mm accuracy. Micrometers are another type of measuring tool that are used to measure very small distances, typically up to 25mm. They offer higher accuracy compared to vernier calipers and can measure to within 0.001mm accuracy.

Thread gauges are used to measure the pitch and diameter of threads, while bore gauges are used to measure the internal diameter of holes. Dial gauges are used to measure the depth or distance of features, while surface plates are flat and level surfaces used as reference standards for measuring flatness, parallelism, and squareness. Height gauges are used to measure the height of parts and features relative to a reference surface.
In addition to selecting the right measuring tools for a CNC machine, it is important to use proper measuring techniques and procedures. This includes proper calibration and zeroing of measuring instruments, as well as regular inspection and maintenance to ensure accurate and reliable measurements.
Some CNC machines may also be equipped with automated measuring systems, such as touch probes and laser measurement systems. These systems can help to reduce setup times and improve part accuracy by automatically measuring part features and comparing them to the CAD model.
Overall, selecting the right measuring equipment and using proper measuring techniques is essential for achieving precision and accuracy in CNC machining operations. With the right tools and procedures in place, machinists can ensure that parts are produced to the highest quality standards.
5. Work offset and tool measuring system
Work offset and tool measuring systems allow machinists to accurately position workpieces and measure tool offsets for precise machining operations. There are a variety of systems available for work offset and tool measurement, including tool presetter, edge finders, and probes.
Tool presetters are used to measure and set the tool length and diameter off the machine, allowing for faster and more accurate tool changes. This can significantly reduce setup times and improve overall machining efficiency. Edge finders are used to precisely locate the edges of workpieces, allowing machinists to set the work offset and accurately position the workpiece in the machine.
Probes are another type of tool measuring system that can be used for both work offset and tool measurement. They can be used to measure the length and diameter of tools, as well as the position of workpieces in the machine. This information can be used to automatically adjust the machining program, ensuring that the tool is positioned correctly for the desired operation.

In addition to improving efficiency and accuracy, work offset and tool measuring systems can also help to reduce scrap and rework by ensuring that parts are machined to the correct specifications. Proper use and calibration of these systems is critical for achieving optimal results.
Some CNC machines may also be equipped with advanced tool measurement systems, such as laser tool measurement and camera-based tool measurement. These systems can provide even higher levels of accuracy and efficiency by automatically measuring tools and updating the machining program.
Overall, work offset and tool measuring systems are essential components of CNC machining, allowing machinists to achieve high levels of accuracy and efficiency in their operations. By selecting the right system for the job and using proper calibration and measurement techniques, machinists can maximize the performance of their CNC machines and produce high-quality parts.
6. Safety Equipment
CNC machining can be a hazardous process, and safety equipment is essential to protect workers and machinery. There are a variety of safety equipment options available for CNC machining, including personal protective equipment (PPE), machine guards, and safety sensors.
PPE is the first line of defense against injury in CNC machining, and includes items such as safety glasses, gloves, hearing protection, and respirators. It is important for workers to wear the appropriate PPE for the specific machining operation being performed.
Machine guards are physical barriers that protect workers from moving machine parts and flying debris. They are commonly used on lathes, milling machines, and other CNC machines to prevent accidents and injuries. It is important to properly install and maintain machine guards to ensure their effectiveness.
Safety sensors are electronic devices that monitor the operation of CNC machines and shut them down if a safety hazard is detected. They can detect things like tool breakage, abnormal vibration, and coolant levels, and can prevent serious accidents and damage to the machine. Properly maintaining and testing safety sensors is critical for ensuring their effectiveness.
In addition to these specific safety equipment options, it is important to have general safety protocols in place, such as regular machine inspections, safety training for workers, and clear procedures for handling hazardous materials.
Overall, safety equipment is critical to protect workers and machinery in CNC machining operations. By selecting the appropriate PPE, machine guards, and safety sensors, and implementing proper safety protocols, machinists can reduce the risk of accidents and injuries and ensure a safe and productive workplace.
7. Choosing the Right Coolant and Cutting Fluid
Coolant and cutting fluid help to improve the quality of the finished product, increase tool life, and prevent machine wear. There are several types of coolants and cutting fluids available for CNC machines, each with its own unique properties and benefits.
Water-soluble coolants are a popular choice for CNC machining operations. They are versatile, effective, and easy to use. They are also cost-effective and can be used with a variety of different metals and materials. Water-soluble coolants can help to reduce heat buildup during machining operations, which can improve the quality of the finished product and increase tool life.
Synthetic coolants are another popular option for CNC machining. They are designed to be long-lasting and provide superior lubrication for cutting tools. They are also more stable than water-soluble coolants and can resist bacterial growth, which can reduce the risk of machine downtime and maintenance.
Cutting fluids are another important component of CNC machining. They are designed to provide lubrication for cutting tools and reduce heat buildup during machining operations. There are several types of cutting fluids available, including mineral oil-based fluids, synthetic fluids, and semi-synthetic fluids.
In addition to coolants and cutting fluids, hydraulic oils are also essential for CNC machines that use hydraulic systems. Hydraulic oils are designed to provide lubrication and protection for hydraulic components, and can help to prevent wear and extend the life of the hydraulic system.
When choosing a coolant, cutting fluid, or hydraulic oil for your CNC machine, it is important to consider factors such as the materials being machined, the machining process being used, and the specific requirements of the machine. By selecting the right coolant and cutting fluid for your CNC machine, you can improve the quality of the finished product, increase tool life, and reduce the risk of machine wear and downtime.
8. CAD/CAM and Reporting Software
CAD software is used to create detailed 3D models of parts or products, while CAM software is used to generate the tool paths and machining instructions that are used by the CNC machine.
There are many different CAD/CAM software options available, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Some popular options include SolidWorks, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360. These software programs allow designers and engineers to create detailed 3D models of parts or products, and then use CAM software to generate the tool paths and machining instructions that are used by the CNC machine.
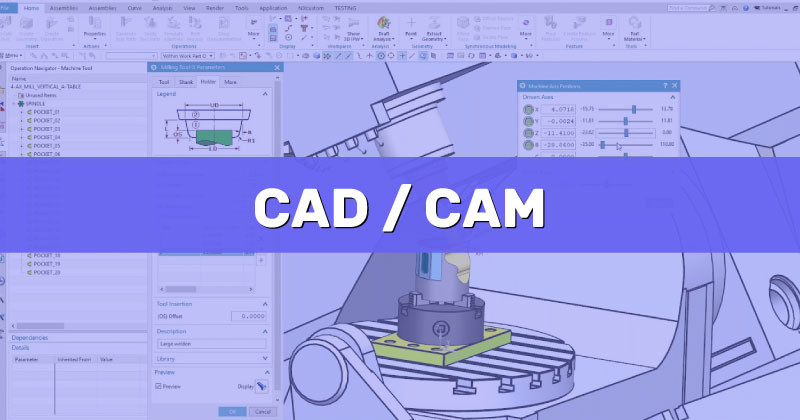
In addition to CAD/CAM software, reporting software is also an important component of CNC machining. Reporting software allows users to collect and analyze data about the machining process, including information about tool wear, cycle time, and other key metrics. This data can then be used to optimize the machining process, improve quality control, and reduce costs.
Some popular reporting software options for CNC machines include MDC-Max and MachineMetrics. These software programs allow users to collect and analyze data in real-time, which can help to identify potential issues or inefficiencies in the machining process.
When selecting CAD/CAM or reporting software for your CNC machine, it is important to consider factors such as compatibility with your machine, ease of use, and the specific needs of your machining operation. By using the right software, you can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your CNC machining process, while also reducing costs and improving quality control.
9. Chip Conveyors and Chip Transfer
CNC machines generate a large amount of chips and debris during the machining process. If these chips and debris are not properly managed, they can cause a range of issues, including damage to the machine, reduced machining accuracy, and increased downtime. This is where chip conveyors and chip transfer systems come in.
A chip conveyor is a mechanical system that is used to collect and remove chips and debris from the machining area of a CNC machine. The conveyor system typically consists of a series of belts or chains that transport the chips and debris away from the machine and into a collection bin or other disposal area.
Chip transfer systems, on the other hand, are used to separate and manage different types of chips and debris generated during the machining process. Different types of metals, for example, require different disposal methods and may even have different resale values. Chip transfer systems can help to separate these different types of chips and debris, making it easier to manage and dispose of them.
Properly managing chips and debris is critical to the performance and longevity of CNC machines. A chip conveyor and chip transfer system can help to prevent damage to the machine, improve machining accuracy, and reduce downtime. Additionally, separating and managing different types of chips and debris can help to increase their resale value and reduce disposal costs.
When selecting a chip conveyor or chip transfer system, it is important to consider factors such as the size and type of the CNC machine, the type of machining operation, and the type of chips and debris that will be generated. By selecting the right system, you can help to ensure the long-term performance and reliability of your CNC machine, while also reducing costs and improving efficiency.
10. Essential Maintenance Tools
Proper maintenance is important to the long-term performance and reliability of CNC machines. Regular maintenance helps to prevent breakdowns, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of the machine. To perform maintenance effectively, it is important to have the right tools on hand. Here are some essential maintenance tools for CNC machines:
Allen wrenches - CNC machines are often assembled using bolts and screws that require an Allen wrench. Having a set of different sizes of Allen wrenches on hand can help you to easily access and remove these fasteners when performing maintenance.
Screwdrivers - In addition to Allen wrenches, having a set of screwdrivers with different sizes and types of tips is important for accessing and removing different types of screws and fasteners.
Cleaning supplies - Regular cleaning of a CNC machine is essential for maintaining its performance and longevity. Some common cleaning supplies include cleaning solution, rags, and brushes.
Lubricants - CNC machines have many moving parts that require lubrication to operate smoothly. Having a supply of appropriate lubricants on hand can help to ensure the long-term performance and reliability of the machine.
Torque wrench - Properly tightening bolts and screws to the correct torque specification is important for ensuring the safety and reliability of the CNC machine. A torque wrench can help to ensure that fasteners are tightened to the appropriate level.
Diagnostic tools - Having diagnostic tools on hand, such as multimeters or oscilloscopes, can help to troubleshoot and diagnose issues with the CNC machine.
Replacement parts - Having a supply of commonly used replacement parts, such as belts, bearings, and fuses, can help to quickly replace worn or damaged components during maintenance.
By having the right maintenance tools on hand, you can perform maintenance on your CNC machine efficiently and effectively, helping to ensure its long-term performance and reliability. Regular maintenance, along with the proper use of these tools, can help to prevent costly breakdowns and minimize downtime, ultimately saving you time and money in the long run.
11. Tool and Machined Part Storage
In CNC machining, the storage and organization of tools and finished parts is critical for maximizing efficiency and productivity. A well-planned tool storage system ensures that the necessary tools are easily accessible and in good condition, reducing the time and effort required to set up for machining operations. Similarly, an organized system for storing finished parts after machining prevents damage and facilitates quick retrieval for subsequent operations.
There are several types of tool storage systems available, ranging from simple racks and cabinets to sophisticated automated systems. The choice of tool storage system depends on factors such as the type and volume of tools, available space, and budget. Some common types of tool storage include tool carts, tool cribs, and tool vending machines.
Finished part storage is equally important, especially for high-volume production runs. Properly labeled and organized storage bins or shelves help prevent damage to finished parts and simplify inventory management. Depending on the type and size of finished parts, specialized storage solutions such as trays, racks, or drawers may be necessary.
Implementing an efficient tool and finished part storage system can significantly improve the overall efficiency and productivity of a CNC machining operation. It is essential to regularly evaluate and optimize the storage system to ensure it meets the evolving needs of the manufacturing process.
Final Thoughts
By following our tips and information, you'll have everything you need to set up your new CNC machine with confidence. From basic tooling to advanced solutions, work holding, measuring equipment, and more, we've got you covered. Invest in quality equipment, follow best practices for maintenance and safety, and you'll be on your way to achieving your production goals. Start planning your setup today and unlock your operation's full potential.




